Document Legalisation Info & Articles #apostille
Articles and handy information regarding document Legalisation, Apostilles, Authentication, Embassy Attestation in South-Africa
An Apostille is a certificate that authenticates the origin of a public document (e.g., a birth, marriage or death certificate, a judgment, an extract of a register or a notarial attestation). T
Read MoreThe apostille certificate is attached and sealed to another document that is required in another country. This is done as a failsafe against tampering. After a document has been checked and the signatures or stamps have been verified the apostille can be issued.
Read MoreA South Africa public documents must be legalised or authenticated using the Apostille Certificate if the the destination country have subscribed to the Apostille Convention. South Africa is a subscribing country to the Hague Apostille Convention
Read MoreThe Apostille of the Hague is a stamp that proves that a document obtained in a country is true and, therefore, must be recognized and accepted as valid in another. The apostille process consists of placing on an official document, or an extension thereof, an Apostille or annotation that will certify the authenticity of the signature of the public documents issued in a signatory country of the XII Hague Convention
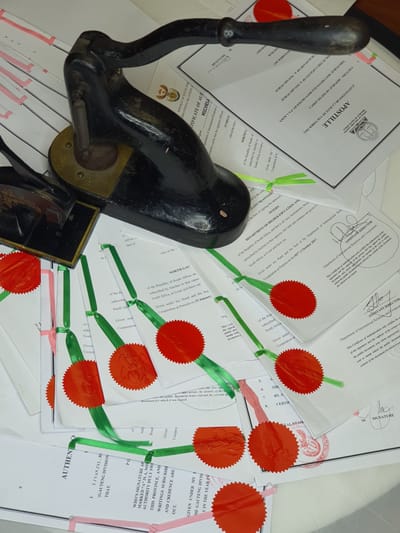
Read MoreAn Apostille is an bound page that is attached to your original document (e.g. birth certificate) stating that the person issuing and/or signing the document is legitimate, as well as the stamp thereupon. The Apostille page is attached by a ribbon, verifying the signature on the document and/or the stamp affixed thereto.
Read MoreConvention of 5 October 1961 Abolishing the Requirement of Legalisation for Foreign Public Documents (1961 Apostille Convention) entered into force for Saudi Arabia following the deposit of its instrument of accession on 8 April 2022. The 1961 Apostille Convention currently has 124 Contracting Parties. More information on this Convention is available on the Apostille Section of the HCCH website. Saudi Arabia has been a Member of the HCCH since 2016 and the 1,961 Apostille Convention is the first HCCH Convention or instrument it has joined.
Read More